Lingua franca
A lingua franca (; lit. 'Frankish tongue'; for plurals see § Usage notes), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups of people who do not share a native language or dialect, particularly when it is a third language that is distinct from both of the speakers' native languages.
Lingua francas have developed around the world throughout human history, sometimes for commercial reasons (so-called "trade languages" facilitated trade), but also for cultural, religious, diplomatic and administrative convenience, and as a means of exchanging information between scientists and other scholars of different nationalities. The term is taken from the medieval Mediterranean Lingua Franca, a Romance-based pidgin language used especially by traders in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th centuries. A world language—a language spoken internationally and by many people—is a language that may function as a global lingua franca.
Characteristics
Any language regularly used for communication between people who do not share a native language is a lingua franca. Lingua franca is a functional term, independent of any linguistic history or language structure.
Pidgins are therefore lingua francas; creoles and arguably mixed languages may similarly be used for communication between language groups. But lingua franca is equally applicable to a non-creole language native to one nation (often a colonial power) learned as a second language and used for communication between diverse language communities in a colony or former colony.
Lingua francas are often pre-existing languages with native speakers, but they can also be pidgin or creole languages developed for that specific region or context. Pidgin languages are rapidly developed and simplified combinations of two or more established languages, while creoles are generally viewed as pidgins that have evolved into fully complex languages in the course of adaptation by subsequent generations. Pre-existing lingua francas such as French are used to facilitate intercommunication in large-scale trade or political matters, while pidgins and creoles often arise out of colonial situations and a specific need for communication between colonists and indigenous peoples. Pre-existing lingua francas are generally widespread, highly developed languages with many native speakers. Conversely, pidgin languages are very simplified means of communication, containing loose structuring, few grammatical rules, and possessing few or no native speakers. Creole languages are more developed than their ancestral pidgins, utilizing more complex structure, grammar, and vocabulary, as well as having substantial communities of native speakers.
Whereas a vernacular language is the native language of a specific geographical community, a lingua franca is used beyond the boundaries of its original community, for trade, religious, political, or academic reasons. For example, English is a vernacular in the United Kingdom but it is used as a lingua franca in the Philippines, alongside Filipino. Likewise, Arabic, French, Mandarin Chinese, Russian and Spanish serve similar purposes as industrial and educational lingua francas across regional and national boundaries.
Even though they are used as bridge languages, international auxiliary languages such as Esperanto have not had a great degree of adoption, so they are not described as lingua francas.
Etymology
The term lingua franca derives from Mediterranean Lingua Franca (also known as Sabir), the pidgin language that people around the Levant and the eastern Mediterranean Sea used as the main language of commerce and diplomacy from late medieval times to the 18th century, most notably during the Renaissance era. During that period, a simplified version of mainly Italian in the eastern and Spanish in the western Mediterranean that incorporated many loan words from Greek, the Slavic languages, Arabic, and Turkish came to be widely used as the "lingua franca" of the region, although some scholars claim that the Mediterranean Lingua Franca was just poorly used Italian.
In Lingua Franca (the specific language), lingua is from the Italian for 'a language'. Franca is related to Greek Φρᾰ́γκοι (Phránkoi) and Arabic إِفْرَنْجِي (ʾifranjiyy) as well as the equivalent Italian—in all three cases, the literal sense is 'Frankish', leading to the direct translation: 'language of the Franks'. During the late Byzantine Empire, Franks was a term that applied to all Western Europeans. The overall phrase of lingua franca is also speculated to originate from lisan al-Faranja ( لسان الفرنجة) which also means the 'language of the Franks'.
Through changes of the term in literature, lingua franca has come to be interpreted as a general term for pidgins, creoles, and some or all forms of vehicular languages. This transition in meaning has been attributed to the idea that pidgin languages only became widely known from the 16th century on due to European colonization of continents such as The Americas, Africa, and Asia. During this time, the need for a term to address these pidgin languages arose, hence the shift in the meaning of Lingua Franca from a single proper noun to a common noun encompassing a large class of pidgin languages.
As recently as the late 20th century, some restricted the use of the generic term to mean only mixed languages that are used as vehicular languages, its original meaning.
Douglas Harper's Online Etymology Dictionary states that the term Lingua Franca (as the name of the particular language) was first recorded in English during the 1670s, although an even earlier example of the use of it in English is attested from 1632, where it is also referred to as "Bastard Spanish".
Usage notes
The term is well established in its naturalization to English and so major dictionaries do not italicize it as a "foreign" term.
Its plurals in English are lingua francas and linguae francae, with the former being first-listed or only-listed in major dictionaries.
Examples
Historical lingua francas

The use of lingua francas has existed since antiquity.
Akkadian (died out during Classical antiquity) and then Aramaic remained the common languages of a large part of Western Asia from several earlier empires.
Sanskrit historically served as a lingua franca throughout the majority of India and Greater India. The Sanskrit language's historic presence is attested across a wide geography beyond South Asia. Inscriptions and literary evidence suggests that Sanskrit language was already being adopted in Southeast Asia and Central Asia in the 1st millennium CE, through monks, religious pilgrims and merchants.
Until the early 20th century, Classical Chinese served as both the written lingua franca and the diplomatic language in Far East Asia including China, Korea, Japan (includes Taiwan, Ryūkyū), and Vietnam. In the early 20th century, vernacular written Chinese replaced Classical Chinese within China as both the written and spoken lingua franca for speakers of different Chinese dialects, and because of the declining power and cultural influence of China in East Asia, English has since replaced Classical Chinese as the lingua franca in East Asia.
Koine Greek was the lingua franca of the Hellenistic culture. Koine Greek (Modern Greek: Ελληνιστική Κοινή, romanized: Ellinistikí Kiní, lit. 'Common Greek'; Greek: [elinistiˈci ciˈni]), also known as Alexandrian dialect, common Attic, Hellenistic, or Biblical Greek, was the common supra-regional form of Greek spoken and written during the Hellenistic period, the Roman Empire and the early Byzantine Empire. It evolved from the spread of Greek following the conquests of Alexander the Great in the fourth century BC, and served as the lingua franca of much of the Mediterranean region and the Middle East during the following centuries.
Old Tamil was once the lingua franca for most of ancient Tamilakam and Sri Lanka. John Guy states that Tamil was also the lingua franca for early maritime traders from India. The language and its dialects were used widely in the state of Kerala as the major language of administration, literature and common usage until the 12th century AD. Tamil was also used widely in inscriptions found in southern Andhra Pradesh districts of Chittoor and Nellore until the 12th century AD. Tamil was used for inscriptions from the 10th through 14th centuries in southern Karnataka districts such as Kolar, Mysore, Mandya and Bangalore.
Latin through the power of the Roman Republic became the dominant language in Italia and subsequently throughout the realms of Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin was the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition.
Classical Māori was the lingua franca (formed out of many dialects, albeit all mutually intelligible) of both Te Ika-ā-Māui and Te Waipounamu for the 800 years before the European settlement of New Zealand, where it was used for trade, inter-iwi dialogue on marae, and education through wānanga. The period between the 16th and 19th centuries is known as "Te Puawaitanga", or the flowering period, during which time Classical Māori thrived. After the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi, Classical Māori remained the lingua franca of the nascent Colony of New Zealand until English superseded it in the 1870s. The language was initially vital for all European and Chinese migrants in New Zealand to learn, as Māori formed a majority of the population, owned nearly all the country's land and dominated the economy until the 1860s. After the success of the Europeans during the New Zealand Wars and increasing land confiscation drove power into the hands of Pākehā, discriminatory laws such as the Native Schools Act 1867 contributed to the demise of Classical Māori as a lingua franca.
Sogdian was used to facilitate trade between those who spoke different languages along the Silk Road, which is why native speakers of Sogdian were employed as translators in Tang China. The Sogdians also ended up circulating spiritual beliefs and texts, including those of Buddhism and Christianity, thanks to their ability to communicate to many people in the region through their native language.
Old Church Slavonic, an Eastern South Slavic language, is the first Slavic literary language. Between 9th and 11th century, it was lingua franca of great part of the predominantly Slavic states and populations in Southeast and Eastern Europe, in liturgy and church organization, culture, literature, education and diplomacy, as Official language, and National language in the case of Bulgaria. It was the first national and also international Slavic literary language (autonym словѣ́ньскъ ѩꙁꙑ́къ, slověnĭskŭ językŭ). The Glagolitic alphabet was originally used at both schools, though the Cyrillic script was developed early on at the Preslav Literary School, where it superseded Glagolitic as official in Bulgaria in 893. Old Church Slavonic spread to other South-Eastern, Central, and Eastern European Slavic territories, most notably Croatia, Serbia, Bohemia, Lesser Poland, and principalities of the Kievan Rus' while retaining characteristically South Slavic linguistic features. It spread also to not completely Slavic territories between the Carpathian Mountains, the Danube and the Black sea, corresponding to Wallachia and Moldavia. Nowadays, the Cyrillic script writing system is used for various languages across Eurasia and is used as the national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia.
The Mediterranean Lingua Franca was largely based on Italian and Provençal. This language was spoken from the 11th to 19th centuries around the Mediterranean basin, particularly in the European commercial empires of Italian cities (Genoa, Venice, Florence, Milan, Pisa, Siena) and in trading ports located throughout the eastern Mediterranean rim.
During the Renaissance, standard Italian was spoken as a language of culture in the main royal courts of Europe, and among intellectuals. This lasted from the 14th century to the end of the 16th, when French replaced Italian as the usual lingua franca in northern Europe. On the other hand, Italian musical terms, in particular dynamic and tempo notations, have continued in use to the present day, especially for classical music, in music revues and program notes as well as in printed scores. Italian is considered the language of Opera.
Classical Quechua is either of two historical forms of Quechua, the exact relationship and degree of closeness between which is controversial, and which have sometimes been identified with each other. These are:
- the variety of Quechua that was used as a lingua franca and administrative language in the Inca Empire (1438–1533) (or Inca lingua franca). Since the Incas didn't have writing, the evidence about the characteristics of this variety is scant and they have been a subject of significant disagreements.
- the variety of Quechua that was used in writing for religious and administrative purposes in the Andean territories of the Spanish Empire, mostly in the late 16th century and the first half of the 17th century and has sometimes been referred to, both historically and in academia, as lengua general ('common language') (or Standard Colonial Quechua).
Modern
English

English is sometimes described as the first global lingua franca, being used as a working language by individuals of diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds in a variety of fields and international organizations to communicate with one another.
When the United Kingdom became a colonial power, English served as the lingua franca of the colonies of the British Empire. In the post-colonial period, most of the newly created nations which had multiple indigenous languages opted to continue using English as one of their official languages such as Ghana and South Africa. In other former colonies with multiple official languages such as Singapore and Fiji, English is the primary medium of education and serves as the lingua franca among citizens.
Even in countries not associated with the English-speaking world, English has emerged as a lingua franca in certain situations where its usage is perceived to be more efficient to communicate, especially among groups consisting of native speakers of a variety of languages. For example, in Qatar, the medical community is primarily made up of workers from countries without English as a native language. In medical practices and hospitals, nurses typically communicate with other professionals in English as a lingua franca. This occurrence has led to interest in researching the consequences and affordances of the medical community communicating in a lingua franca. English is also sometimes used as a lingua franca in Switzerland, particularly when communicating with people from the country's multiple language communities, or when an interlocutor's level in the native language to whom they are communicating with is weaker.
In the European Union, the use of English as a lingua franca has led researchers to investigate whether a new dialect of English (Euro English) has emerged.
In the fields of technology and science, English emerged as a lingua franca in the 20th century.
Spanish

The Spanish language spread mainly throughout the New World, becoming a lingua franca in the territories and colonies of the Spanish Empire, which also included parts of Africa, Asia, and Oceania. After the breakup of much of the empire in the Americas, its function as a lingua franca was solidified by the governments of the newly independent nations of what is now Hispanic America. While its usage in Spain's Asia-Pacific colonies eventually died out, Spanish became the lingua franca of what is now Equatorial Guinea, being the main language of government and education and is spoken by the vast majority of the population.
Due to large numbers of immigrants from Latin America in the second half of the 20th century and resulting influence, Spanish has also emerged somewhat as a lingua franca in parts of the Southwestern United States and southern Florida, especially in communities where native Spanish speakers form the majority of the population.
At present it is the second most used language in international trade, and the third most used in politics, diplomacy and culture after English and French.
It is also one of the most taught foreign languages throughout the world and is also one of the six official languages of the United Nations.
French

Although not spoken as a first language by most African French speakers, French is a lingua franca in most Western and Central African countries and an official language of many, a remnant of French and Belgian colonialism. These African countries and others are members of the Francophonie. During the 17th century, French replaced Latin as the most important language of diplomacy and international relations (lingua franca). It retained this role until approximately the middle of the 20th century, when it was replaced by English as the United States became the dominant global power following the Second World War. Stanley Meisler of the Los Angeles Times said that the fact that the Treaty of Versailles was written in English as well as French was the "first diplomatic blow" against the language.
German
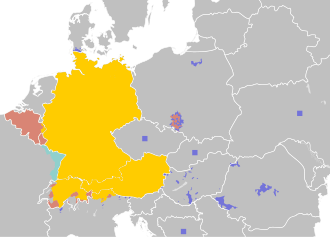
German is used as a lingua franca in Switzerland to some extent; however, English is generally preferred to avoid favouring it over the three other official languages. Middle Low German used to be the Lingua franca during the late Hohenstaufen till the mid 15th century periods, in the North Sea and the Baltic Sea when extensive trading was done by the Hanseatic League along the Baltic and North Seas. German remains a widely studied language in Central Europe and the Balkans, especially in former Yugoslavia. It is recognised as an official language in countries outside of Europe, specifically Namibia.
Arabic

Dark green: majority; light green: significant minority
Arabic was used as a lingua franca across the Islamic empires, whose sizes necessitated the need for a common language, and spread across the Arab and Muslim worlds. In Djibouti and parts of Eritrea, both of which are countries where multiple official languages are spoken, Arabic has emerged as a lingua franca in part thanks to the population of the region being predominantly Muslim and Arabic playing a crucial role in the religion of Islam. In addition, after having fled from Eritrea due to ongoing warfare and gone to some of the nearby Arab countries, Eritrean emigrants are contributing to Arabic becoming a lingua franca in the region by coming back to their homelands having picked up the Arabic language.
Russian
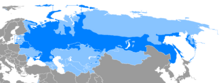
Russian is in use and widely understood in Central Asia and the Caucasus, areas formerly part of the Russian Empire and Soviet Union. Its use remains prevalent in Belarus and Ukraine. Russian has some presence as a minority language in the Baltic states and some parts of Eastern Europe. It remains the official language of the Commonwealth of Independent States. Russian is also one of the six official languages of the United Nations.
Portuguese

Portuguese served as lingua franca in the Portuguese Empire, Africa, South America and Asia in the 15th and 16th centuries. When the Portuguese started exploring the seas of Africa, America, Asia and Oceania, they tried to communicate with the natives by mixing a Portuguese-influenced version of lingua franca with the local languages. When Dutch, English or French ships came to compete with the Portuguese, the crews tried to learn this "broken Portuguese". Through a process of change the lingua franca and Portuguese lexicon was replaced with the languages of the people in contact. Portuguese remains an important lingua franca in the Portuguese-speaking African countries, East Timor, and to a certain extent in Macau where it is recognized as an official language alongside Chinese though in practice not commonly spoken.
Chinese
Today, Mandarin Chinese is the lingua franca of China and Taiwan, which are home to many mutually unintelligible varieties of Chinese and, in the case of Taiwan, indigenous Formosan languages. It is also used as a lingua franca and language of education among various Chinese diaspora communities, particularly in Southeast Asia.
Hindustani
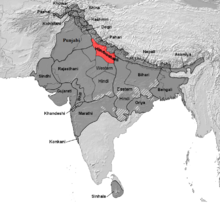
The Hindustani language (Hindi-Urdu) is the lingua franca of Pakistan and Northern India. Many Hindi speaking North Indian states have adopted the Three-language formula in which students are taught: "(a) Hindi (with Sanskrit as part of the composite course); (b) Any other modern Indian language including Urdu and (c) English or any other modern European language." The order in non-Hindi speaking states is: "(a) the major language of the state or region; (b) Hindi; (c) Any other modern Indian language including Urdu but excluding (a) and (b) above; and (d) English or any other modern European language." Hindi has also emerged as a lingua franca for the locals of Arunachal Pradesh, a linguistically diverse state in Northeast India. It is estimated that 90 percent of the state's population knows Hindi.
Malay
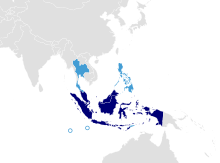
Malay is understood across a cultural region in Southeast Asia called the "Malay world" including Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Southern Thailand, and certain parts of Philippines. It is pluricentric, with several nations codifying a local vernacular variety into several national literary standards: Indonesia notably adopts a variant spoken in Riau specifically as the basis for "Indonesian" for national use despite Javanese having more native speakers; this standard is the sole official language spoken throughout the vast country despite being the first language of some Indonesians.
Swahili

Swahili developed as a lingua franca between several Bantu-speaking tribal groups on the east coast of Africa with heavy influence from Arabic. The earliest examples of writing in Swahili are from 1711. In the early 19th century the use of Swahili as a lingua franca moved inland with the Arabic ivory and slave traders. It was eventually adopted by Europeans as well during periods of colonization in the area. German colonizers used it as the language of administration in German East Africa, later becoming Tanganyika, which influenced the choice to use it as a national language in what is now independent Tanzania. Swahili (known to natives as Kiswahili) is currently one of the national languages and it is taught in schools and universities in several East African countries, thus prompting it to be regarded as a modern-day lingua franca by many people in the region. Several Pan-African writers and politicians have unsuccessfully called for Swahili to become the lingua franca of Africa as a means of unifying the African continent and overcoming the legacy of colonialism.
Persian
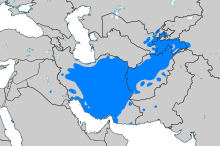
Persian, an Iranian language, is the official language of Iran, Afghanistan (Dari) and Tajikistan (Tajik). It acts as a lingua franca in both Iran and Afghanistan between the various ethnic groups in those countries. The Persian language in South Asia, before the British colonized the Indian subcontinent, was the region's lingua franca and a widely used official language in north India and Pakistan.
Hausa
Hausa can also be seen as a lingua franca because it is the language of communication between speakers of different languages in Northern Nigeria and other West African countries, including the northern region of Ghana.
Amharic
Amharic is the lingua franca and most widely spoken language in Ethiopia and is known by most people who speak another Ethiopian language.
Creole languages
Creoles, such as Nigerian Pidgin in Nigeria, are used as lingua francas across the world. This is especially true in Africa, the Caribbean, Melanesia, Southeast Asia and in parts of Australia by Indigenous Australians.
Sign languages

The majority of pre-colonial North American nations communicated internationally using Hand Talk. Also called Prairie Sign Language, Plains Indian Sign Language, or First Nations Sign Language, this language functioned predominantly—and still continues to function—as a second language within most of the (now historical) countries of the Great Plains, from Newe Segobia in the West to Anishinaabewaki in the East, down into what are now the northern states of Mexico and up into Cree Country stopping before Denendeh. The relationship remains unknown between Hand Talk and other manual Indigenous languages like Keresan Sign Language and Plateau Sign Language, the latter of which is now extinct (though Ktunaxa Sign Language is still used). Although unrelated, perhaps Inuit Sign Language played and continues to play a similar role across Inuit Nunangat and the various Inuit dialects. The original Hand Talk is found across Indian Country in pockets, but it has also been employed to create new or revive old languages, such as with Oneida Sign Language.
International Sign, though a pidgin language, is present at most significant international gatherings, from which interpretations of national sign languages are given, such as in LSF, ASL, BSL, Libras, or Auslan. International Sign, or IS and formerly Gestuno, interpreters can be found at many European Union parliamentary or committee sittings, during certain United Nations affaires, conducting international sporting events like the Deaflympics, in all World Federation of the Deaf functions, and across similar settings. The language has few set internal grammatical rules, instead co-opting national vocabularies of the speaker and audience, and modifying the words to bridge linguistic gaps, with heavy use of gesture and classifiers.
See also
- Rosetta Stone
- Global language system
- International auxiliary language
- Koiné language
- Language contact
- List of languages by number of native speakers
- List of languages by total number of speakers
- List of languages by the number of countries in which they are recognized as an official language
- Mixed language
- Pidgin
- Pluricentric language
- Interlinguistics
- Universal language
- Vernacular
- Working language
- World language