English-speaking world
The English-speaking world comprises the 88 countries and territories where English is either an official, administrative, or cultural language. As of the 2000s, between one billion to two billion people globally speak English, making it the largest language by number of speakers, and the third largest language by number of native speakers, as well as the most geographically widespread language. The regions where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population, due to cultural connections to England, are termed "the Anglosphere". Speakers of English are called Anglophones.
England and the Scottish Lowlands, countries of the United Kingdom, are the birthplace of the English language, and the modern form of the language has been spread around the world since the 17th century, first by the worldwide influence of England and later the United Kingdom, and then by that of the United States. Through all types of printed and electronic media of these countries, English has become the leading language of international discourse and the lingua franca in many regions and professional contexts such as science, navigation and law.
The United States and India have the most total English speakers, with 306 million and 265 million, respectively. These are followed by Pakistan (104 million), the United Kingdom (68 million), and Nigeria (60 million). As of 2022, there were about 400 million native speakers of English. When factoring in those who speak English as a second language, estimates of the total number of Anglophones vary greatly, from 1.5 billion to 2 billion. David Crystal calculates that as of 2003 non-native speakers outnumbered native speakers by a ratio of 3:1.
Besides the major varieties of English, namely American, British, Canadian, Australian, Irish, New Zealand English, and their sub-varieties, countries such as South Africa, India, Nigeria, the Philippines, Singapore, Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago also have millions of native speakers of dialect continua ranging from English-based creole languages to Standard English. Other countries and territories, such as Ghana, also use English as their primary official language even if it is not the native language of the majority of the population.
Majority English-speaking countries

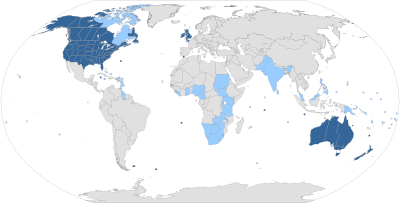
English is the primary natively spoken language in several countries and territories. Five of the largest of these are sometimes described as the "core Anglosphere"; they are the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.
The term "Anglosphere" can sometimes be extended to include other countries and territories where English or an English Creole language is also the primary native language and English is the primary language of government and education, such as Ireland, Gibraltar, and the Commonwealth Caribbean.
While English is also spoken by a majority of people as a second language in a handful of countries such as Denmark, the Netherlands, and Sweden, these countries are not considered part of the English-speaking world as the language is still viewed primarily as a foreign tongue and does not serve an important cultural role in society.
Countries where English is an official language
English is an official language (de facto and de jure) of the following countries and territories.
- North America: Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Canada, Cayman Islands, Curaçao, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Montserrat, Puerto Rico, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, Turks and Caicos Islands, United States, United States Virgin Islands
- South America: Falkland Islands, Guyana
- Europe: Akrotiri and Dhekelia, Gibraltar, Guernsey, Ireland, Isle of Man, Jersey, Malta, United Kingdom
- Africa: Botswana, Cameroon, Eswatini, Gambia, Ghana, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Malawi, Mauritius, Namibia, Nigeria, Rwanda, Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, Sierra Leone, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe
- Asia: Christmas Island, Cocos (Keeling) Islands, Hong Kong, India, Pakistan, Philippines, Singapore
- Oceania: Australia, American Samoa, Cook Islands, Fiji, Guam, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Nauru, New Zealand, Niue, Norfolk Island, Northern Mariana Islands, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Pitcairn Islands, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tokelau, Tuvalu, Vanuatu
Although not official, English is also an important language in some former colonies and protectorates of the British Empire where it is used as an administrative language, such as Bahrain, Brunei, Egypt, Kuwait, Malaysia Qatar, Sri Lanka and United Arab Emirates.
English as a global language
Because English is so widely spoken, it has often been referred to as a "world language", the lingua franca of the modern era, and while it is not an official language in most countries, it is currently the language most often taught as a foreign language. It is, by international treaty, the official language for aeronautical and maritime communications. English is one of the official languages of the United Nations and many other international organizations, including the International Olympic Committee. It is also one of two co-official languages for astronauts (besides the Russian language) serving on board the International Space Station.
English is studied most often in the European Union, and the perception of the usefulness of foreign languages among Europeans is 67% in favour of English ahead of 17% for German and 16% for French (as of 2012). Among some of the non-English-speaking EU countries, the following percentages of the adult population claimed to be able to converse in English in 2012: 90% in the Netherlands, 89% in Malta, 86% in Sweden and Denmark, 73% in Cyprus, Croatia, and Austria, 70% in Finland, and over 50% in Greece, Belgium, Luxembourg, Slovenia, and Germany. In 2012, excluding native speakers, 38% of Europeans consider that they can speak English.
Books, magazines, and newspapers written in English are available in many countries around the world, and English is the most commonly used language in the sciences with Science Citation Index reporting as early as 1997 that 95% of its articles were written in English, even though only half of them came from authors in English-speaking countries.
In publishing, English literature predominates considerably with 28% of all books published in the world [Leclerc 2011] and 30% of web content in 2011 (down from 50% in 2000).
This increasing use of the English language globally has had a large impact on many other languages, leading to language shift and even language death, and to claims of linguistic imperialism. English itself has become more open to language shift as multiple regional varieties feed back into the language as a whole.