Nasalis muscle
| Nasalis muscle | |
|---|---|
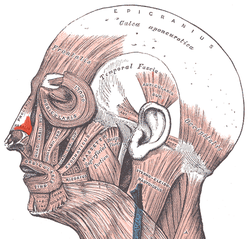 Muscles of the head, face, and neck. (Nasalis labeled at center left.)
| |
| Details | |
| Origin | maxilla |
| Insertion | nasal bone |
| Artery | superior labial artery |
| Nerve | buccal branch of the facial nerve |
| Actions | compresses bridge of nose, depresses tip of nose, elevates corners of nostrils |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus nasalis |
| TA98 | A04.1.03.009 |
| TA2 | 2062 |
| FMA | 46770 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The nasalis muscle is a sphincter-like muscle of the nose. It has a transverse part and an alar part. It compresses the nasal cartilages, and can "flare" the nostrils. It can be used to test the facial nerve (VII), which supplies it.
Structure
The nasalis muscle covers the nasal cartilages of the lower surface of the nose. It consists of two parts, transverse and alar:
- The transverse part (compressor naris muscle) arises from the maxilla, above and lateral to the incisive fossa. Its fibers proceed upward and medially, expanding into a thin aponeurosis which is continuous on the bridge of the nose with that of the muscle of the opposite side, and with the aponeurosis of the procerus muscle. It compresses the nostrils and may completely close them.
- The alar part (dilator naris muscle) arises from the maxilla over the lateral incisor and inserts into the greater alar cartilage. Its medial fibres tend to blend with the depressor septi nasi muscle, and has been described as part of that muscle.
Nerve supply
Like all the other muscles of facial expression, the nasalis muscle is supplied by the facial nerve (VII).
Function
The nasalis muscle compresses the nasal cartilages. It may also "flare" the nostrils.
Clinical significance
Cleft lip and cleft palate
The nasalis muscle is one of the key muscles not formed or inserted correctly with cleft lip and cleft palate deformity. The head of the transverse part needs to be identified during reconstructive surgery so that it can be surgically sutured (connected to) the nasal septum. The origin at the maxilla may also be repositioned for better symmetry.
Facial nerve testing
Due to it being superficial, the nasalis muscle can be used to test the facial nerve. Specifically, it can be used to test the zygomatic branches.
Additional images
-
-

-
-
-
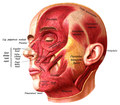
 Position of nasalis muscle (shown in red).
Position of nasalis muscle (shown in red). -
 Left maxilla. Outer surface.
Left maxilla. Outer surface.





