Mylohyoid nerve
| Mylohyoid nerve | |
|---|---|

Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve. (Label for mylohyoid nerve is at bottom center.)
| |
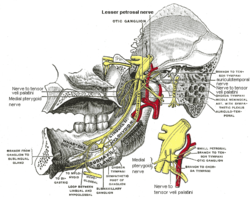 Mandibular division of trifacial nerve, seen from the middle line. The small figure is an enlarged view of the otic ganglion. (Label "to mylohyoid" at bottom left.)
| |
| Details | |
| From | inferior alveolar nerve |
| Innervates | mylohyoid muscle, anterior belly of digastric muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus mylohyoideus |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.090 |
| TA2 | 6275 |
| FMA | 53247 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The mylohyoid nerve (or nerve to mylohyoid) is a mixed nerve of the head. It is a branch of the inferior alveolar nerve. It provides motor innervation the mylohyoid muscle, and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. It provides sensory innervation to part of the submental area, and sometimes also the mandibular (lower) molar teeth, requiring local anaesthesia for some oral procedures.
Structure
Origin
The mylohyoid nerve is a mixed (motor-sensory) branch of the inferior alveolar nerve (which is a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that is itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It arises just before it enters the mandibular foramen.
Course
It pierces the sphenomandibular ligament. It descends in a groove on the deep surface of the ramus of the mandible. When it reaches the under surface of the mylohyoid muscle, it gives branches to the mylohyoid muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle.
Distribution
Motor
The mylohyoid nerve supplies the mylohyoid muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle.
Sensory
It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the centre of the submental area. It may also provide some sensory innervation to the mandibular (lower) molar teeth.
Clinical significance
The mylohyoid nerve needs to be blocked during local anaesthesia of the mandibular (lower) teeth to prevent pain during oral procedures. It may not be anaesthetised during a block of the inferior alveolar nerve, causing pain.
Additional images
-
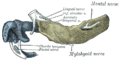 Mandible of human embryo 24 mm. long. Outer aspect.
Mandible of human embryo 24 mm. long. Outer aspect. -
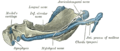 Mandible of human embryo 95 mm. long. Inner aspect. Nuclei of cartilage stippled.
Mandible of human embryo 95 mm. long. Inner aspect. Nuclei of cartilage stippled. -
Infratemporal fossa. Lingual and inferior alveolar nerve. Deep dissection. Anterolateral view


