Libertarianism
Libertarianism (from French: libertaire, itself from the Latin: libertas, lit. 'freedom') is a political philosophy that upholds liberty as a core value. Libertarians seek to maximize autonomy and political freedom, emphasizing equality before the law and civil rights to freedom of association, freedom of speech, freedom of thought and freedom of choice. Libertarians are often skeptical of or opposed to authority, state power, warfare, militarism and nationalism, but some libertarians diverge on the scope of their opposition to existing economic and political systems. Various schools of libertarian thought offer a range of views regarding the legitimate functions of state and private power. Different categorizations have been used to distinguish various forms of Libertarianism. Scholars distinguish libertarian views on the nature of property and capital, usually along left–right or socialist–capitalist lines. Libertarians of various schools were influenced by liberal ideas.
In the mid-19th century, libertarianism originated as a form of left-wing politics such as anti-authoritarian and anti-state socialists like anarchists, especially social anarchists, but more generally libertarian communists/Marxists and libertarian socialists. These libertarians sought to abolish capitalism and private ownership of the means of production, or else to restrict their purview or effects to usufruct property norms, in favor of common or cooperative ownership and management, viewing private property as a barrier to freedom and liberty. While all libertarians support some level of individual rights, left-libertarians differ by supporting an egalitarian redistribution of natural resources. Left-libertarian ideologies include anarchist schools of thought, alongside many other anti-paternalist and New Left schools of thought centered around economic egalitarianism as well as geolibertarianism, green politics, market-oriented left-libertarianism and the Steiner–Vallentyne school. After the fall of the Soviet Union, libertarian socialism grew in popularity and influence as part of anti-war, anti-capitalist and anti- and alter-globalisation movements.
In the mid-20th century, American right-libertarian proponents of anarcho-capitalism and minarchism co-opted the term libertarian to advocate laissez-faire capitalism and strong private property rights such as in land, infrastructure and natural resources. The latter is the dominant form of libertarianism in the United States. This new form of libertarianism was a revival of classical liberalism in the United States, which occurred due to American liberals' embracing progressivism and economic interventionism in the early 20th century after the Great Depression and with the New Deal. Since the 1970s, right-libertarianism has spread beyond the United States, with right-libertarian parties being established in the United Kingdom, Israel, South Africa and Argentina. Minarchists advocate for night-watchman states which maintain only those functions of government necessary to safeguard natural rights, understood in terms of self-ownership or autonomy, while anarcho-capitalists advocate for the replacement of all state institutions with private institutions. Some right-wing variants of libertarianism, such as anarcho-capitalism, has been labeled as far-right or radical right by some scholars. Right-wing libertarian ideals are also prominent in far-right American militia movement associated with extremist anti-government ideas.
Traditionally, libertarian practice has taken extraparliamentary form, such as in the Spanish Revolution of 1936, the New Left, the Zapatista uprising, the Tea Party movement, and the Rojava Revolution. In 2022, student activist and self-described libertarian socialist Gabriel Boric became head of state of Chile after winning the 2021 Chilean presidential election with the Apruebo Dignidad coalition. In 2023, Argentine economist Javier Milei became the first open right-wing libertarian head of state, after winning that year's general election with the La Libertad Avanza coalition.
Overview
Etymology

The first recorded use of the term libertarian was in 1789, when William Belsham wrote about libertarianism in the context of metaphysics. As early as 1796, libertarian came to mean an advocate or defender of liberty, especially in the political and social spheres, when the London Packet printed on 12 February the following: "Lately marched out of the Prison at Bristol, 450 of the French Libertarians". It was again used in a political sense in 1802 in a short piece critiquing a poem by "the author of Gebir" and has since been used with this meaning.
The use of the term libertarian to describe a new set of political positions has been traced to the French cognate libertaire, coined in a letter French libertarian communist Joseph Déjacque wrote to mutualist Pierre-Joseph Proudhon in 1857. Déjacque also used the term for his anarchist publication Le Libertaire, Journal du mouvement social (Libertarian: Journal of Social Movement) which was printed from 9 June 1858 to 4 February 1861 in New York City. Sébastien Faure, another French libertarian communist, began publishing a new Le Libertaire in the mid-1890s while France's Third Republic enacted the so-called villainous laws (lois scélérates) which banned anarchist publications in France. Libertarianism has frequently been used to refer to anarchism and libertarian socialism since this time.
In the United States, libertarian was popularized by the individualist anarchist Benjamin Tucker around the late 1870s and early 1880s. Libertarianism as a synonym for liberalism was popularized in May 1955 by writer Dean Russell, a colleague of Leonard Read and a classical liberal himself. Russell justified the choice of the term as follows:
Many of us call ourselves "liberals." And it is true that the word "liberal" once described persons who respected the individual and feared the use of mass compulsions. But the leftists have now corrupted that once-proud term to identify themselves and their program of more government ownership of property and more controls over persons. As a result, those of us who believe in freedom must explain that when we call ourselves liberals, we mean liberals in the uncorrupted classical sense. At best, this is awkward and subject to misunderstanding. Here is a suggestion: Let those of us who love liberty trade-mark and reserve for our own use the good and honorable word "libertarian."
Subsequently, a growing number of Americans with classical liberal beliefs began to describe themselves as libertarians. One person responsible for popularizing the term libertarian in this sense was Murray Rothbard, who started publishing libertarian works in the 1960s. Rothbard described this modern use of the words overtly as a "capture" from his enemies, writing that "for the first time in my memory, we, 'our side,' had captured a crucial word from the enemy. 'Libertarians' had long been simply a polite word for left-wing anarchists, that is for anti-private property anarchists, either of the communist or syndicalist variety. But now we had taken it over".
In the 1970s, Robert Nozick was responsible for popularizing this usage of the term in academic and philosophical circles outside the United States, especially with the publication of Anarchy, State, and Utopia (1974), a response to social liberal John Rawls's A Theory of Justice (1971). In the book, Nozick proposed a minimal state on the grounds that it was an inevitable phenomenon which could arise without violating individual rights.
According to common United States meanings of conservative and liberal, libertarianism in the United States has been described as conservative on economic issues (economic liberalism and fiscal conservatism) and liberal on personal freedom (civil libertarianism and cultural liberalism). It is also often associated with a foreign policy of non-interventionism.
Definition

Although libertarianism originated as a form of left-wing politics, the development in the mid-20th century of modern libertarianism in the United States resulted in libertarianism's being commonly associated with right-wing politics. It also resulted in several authors and political scientists using two or more categorizations to distinguish libertarian views on the nature of property and capital, usually along left–right or socialist–capitalist lines. Right-libertarians reject the label due to its association with conservatism and right-wing politics, calling themselves simply libertarians, while proponents of free-market anti-capitalism in the United States consciously label themselves as left-libertarians and see themselves as being part of a broad libertarian left.
While the term libertarian has been largely synonymous with anarchism as part of the left, continuing today as part of the libertarian left in opposition to the moderate left such as social democracy or authoritarian and statist socialism, its meaning has more recently diluted with wider adoption from ideologically disparate groups, including the right. As a term, libertarian can include both the New Left Marxists (who do not associate with a vanguard party) and extreme liberals (primarily concerned with civil liberties) or civil libertarians. Additionally, some libertarians use the term libertarian socialist to avoid anarchism's negative connotations and emphasize its connections with socialism.
The revival of free-market ideologies during the mid- to late 20th century came with disagreement over what to call the movement. While many of its adherents prefer the term libertarian, many conservative libertarians reject the term's association with the 1960s New Left and its connotations of libertine hedonism. The movement is divided over the use of conservatism as an alternative. Those who seek both economic and social liberty would be known as liberals, but that term developed associations opposite of the limited government, low-taxation, minimal state advocated by the movement. Name variants of the free-market revival movement include classical liberalism, economic liberalism, free-market liberalism and neoliberalism. As a term, libertarian or economic libertarian has the most colloquial acceptance to describe a member of the movement, with the latter term being based on both the ideology's primacy of economics and its distinction from libertarians of the New Left.

While both historical libertarianism and contemporary economic libertarianism share general antipathy towards power by government authority, the latter exempts power wielded through free-market capitalism. Historically, libertarians including Herbert Spencer and Max Stirner supported the protection of an individual's freedom from powers of government and private ownership. In contrast, while condemning governmental encroachment on personal liberties, modern American libertarians support freedoms on the basis of their agreement with private property rights. The abolishment of public amenities is a common theme in modern American libertarian writings.
According to modern American libertarian Walter Block, left-libertarians and right-libertarians agree with certain libertarian premises, but "where [they] differ is in terms of the logical implications of these founding axioms". Although several modern American libertarians reject the political spectrum, especially the left–right political spectrum, several strands of libertarianism in the United States and right-libertarianism have been described as being right-wing, New Right or radical right and reactionary. While some American libertarians such as Walter Block, Harry Browne, Tibor Machan, Justin Raimondo, Leonard Read and Murray Rothbard deny any association with either the left or right, other American libertarians such as Kevin Carson, Karl Hess, and Roderick T. Long have written about libertarianism's left-wing opposition to authoritarian rule and argued that libertarianism is fundamentally a left-wing position. Rothbard himself previously made the same point.
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy defines libertarianism as the moral view that agents initially fully own themselves and have certain moral powers to acquire property rights in external things. Libertarian historian George Woodcock defines libertarianism as the philosophy that fundamentally doubts authority and advocates transforming society by reform or revolution. Libertarian philosopher Roderick T. Long defines libertarianism as "any political position that advocates a radical redistribution of power from the coercive state to voluntary associations of free individuals", whether "voluntary association" takes the form of the free market or of communal co-operatives. According to the American Libertarian Party, libertarianism is the advocacy of a government that is funded voluntarily and limited to protecting individuals from coercion and violence.
Philosophy
According to the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy (IEP), "What it means to be a 'libertarian' in a political sense is a contentious issue, especially among libertarians themselves." Nevertheless, all libertarians begin with a conception of personal autonomy from which they argue in favor of civil liberties and a reduction or elimination of the state. People described as being left-libertarian or right-libertarian generally tend to call themselves simply libertarians and refer to their philosophy as libertarianism. As a result, some political scientists and writers classify the forms of libertarianism into two or more groups to distinguish libertarian views on the nature of property and capital. In the United States, proponents of free-market anti-capitalism consciously label themselves as left-libertarians and see themselves as being part of a broad libertarian left.
Libertarianism is a "[t]heory upholding...[individual] rights...above all else" and seeks to "reduce" the power of a state or states, especially ones a libertarian lives in or is closely associated with, to "safeguard" and maintain individualism.
Libertarians argue that some forms of order within society emerge spontaneously from the actions of many different individuals acting independently from one another without any central planning. Proposed examples of systems which evolved through spontaneous order or self-organization include the evolution of life on Earth, language, crystal structure, the Internet, Wikipedia, workers' councils, Horizontalidad, and a free market economy.
Left-libertarianism
Left-libertarianism encompasses those libertarian beliefs that claim the Earth's natural resources belong to everyone in an egalitarian manner, either unowned or owned collectively. Contemporary left-libertarians such as Hillel Steiner, Peter Vallentyne, Philippe Van Parijs, Michael Otsuka and David Ellerman believe the appropriation of land must leave "enough and as good" for others or be taxed by society to compensate for the exclusionary effects of private property. Socialist libertarians such as social and individualist anarchists, libertarian Marxists, council communists, Luxemburgists and De Leonists promote usufruct and socialist economic theories, including communism, collectivism, syndicalism and mutualism. They criticize the state for being the defender of private property and believe capitalism entails wage slavery and another form of coercion and domination related to that of the state.
There are a number of different left-libertarian positions on the state, which can range from advocating for the complete abolition of the state, to advocating for a more decentralized and limited government with social ownership of the economy. According to Sheldon Richman of the Independent Institute, other left-libertarians "prefer that corporate privileges be repealed before the regulatory restrictions on how those privileges may be exercised."
Right-libertarianism
Right-libertarianism developed in the United States in the mid-20th century from the works of European writers like John Locke, Friedrich Hayek and Ludwig Von Mises and is the most popular conception of libertarianism in the United States today. Commonly referred to as a continuation or radicalization of classical liberalism, the most important of these early right-libertarian philosophers was Robert Nozick. While sharing left-libertarians' advocacy for social freedom, right-libertarians value the social institutions that enforce conditions of capitalism while rejecting institutions that function in opposition to these on the grounds that such interventions represent unnecessary coercion of individuals and abrogation of their economic freedom. Anarcho-capitalists seek the elimination of the state in favor of privately funded security services while minarchists defend night-watchman states which maintain only those functions of government necessary to safeguard natural rights, understood in terms of self-ownership or autonomy.
Libertarian paternalism is a position advocated in the international bestseller Nudge by two American scholars, namely the economist Richard Thaler and the jurist Cass Sunstein. In the book Thinking, Fast and Slow, Daniel Kahneman provides the brief summary: "Thaler and Sunstein advocate a position of libertarian paternalism, in which the state and other institutions are allowed to nudge people to make decisions that serve their own long-term interests. The designation of joining a pension plan as the default option is an example of a nudge. It is difficult to argue that anyone's freedom is diminished by being automatically enrolled in the plan, when they merely have to check a box to opt out". Nudge is considered an important piece of literature in behavioral economics.
Neo-libertarianism combines "the libertarian's moral commitment to negative liberty with a procedure that selects principles for restricting liberty on the basis of a unanimous agreement in which everyone's particular interests receive a fair hearing". Neo-libertarianism has its roots at least as far back as 1980, when it was first described by the American philosopher James Sterba of the University of Notre Dame. Sterba observed that libertarianism advocates for a government that does no more than protection against force, fraud, theft, enforcement of contracts and other negative liberties as contrasted with positive liberties by Isaiah Berlin. Sterba contrasted this with the older libertarian ideal of a night watchman state, or minarchism. Sterba held that it is "obviously impossible for everyone in society to be guaranteed complete liberty as defined by this ideal: after all, people's actual wants as well as their conceivable wants can come into serious conflict. [...] [I]t is also impossible for everyone in society to be completely free from the interference of other persons". In 2013, Sterna wrote that "I shall show that moral commitment to an ideal of 'negative' liberty, which does not lead to a night-watchman state, but instead requires sufficient government to provide each person in society with the relatively high minimum of liberty that persons using Rawls' decision procedure would select. The political program actually justified by an ideal of negative liberty I shall call Neo-Libertarianism".
Libertarian populism combines libertarian and populist politics. According to Jesse Walker, writing in the libertarian magazine Reason, libertarian populists oppose "big government" while also opposing "other large, centralized institutions" and advocate "tak[ing] an axe to the thicket of corporate subsidies, favors, and bailouts, clearing our way to an economy where businesses that can't make money serving customers don't have the option of wringing profits from the taxpayers instead."
Typology
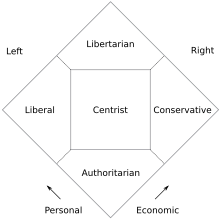
In the United States, libertarian is a typology used to describe a political position that advocates small government and is culturally liberal and fiscally conservative in a two-dimensional political spectrum such as the libertarian-inspired Nolan Chart, where the other major typologies are conservative, liberal and populist. Libertarians support legalization of victimless crimes such as the use of marijuana while opposing high levels of taxation and government spending on health, welfare and education. Libertarians also support a foreign policy of non-interventionism. Libertarian was adopted in the United States, where liberal had become associated with a version that supports extensive government spending on social policies. Libertarian may also refer to an anarchist ideology that developed in the 19th century and to a liberal version which developed in the United States that is avowedly pro-capitalist.
According to polls, approximately one in four Americans self-identify as libertarian. While this group is not typically ideologically driven, the term libertarian is commonly used to describe the form of libertarianism widely practiced in the United States and is the common meaning of the word libertarianism in the United States. This form is often named liberalism elsewhere such as in Europe, where liberalism has a different common meaning than in the United States. In some academic circles, this form is called right-libertarianism as a complement to left-libertarianism, with acceptance of capitalism or the private ownership of land as being the distinguishing feature.
History
Liberalism

Elements of libertarianism can be traced back to the higher-law concepts of the Greeks and the Israelites, and Christian theologians who argued for the moral worth of the individual and the division of the world into two realms, one of which is the province of God and thus beyond the power of states to control it. The right-libertarian economist Murray Rothbard suggested that Chinese Taoist philosopher Laozi was the first libertarian, likening Laozi's ideas on government to Friedrich Hayek's theory of spontaneous order. Similarly, the Cato Institute's David Boaz includes passages from the Tao Te Ching in his 1997 book The Libertarian Reader and noted in an article for the Encyclopædia Britannica that Laozi advocated for rulers to "do nothing" because "without law or compulsion, men would dwell in harmony." Libertarianism was influenced by debates within Scholasticism regarding private property and slavery. Scholastic thinkers, including Thomas Aquinas, Francisco de Vitoria, and Bartolomé de Las Casas, argued for the concept of "self-mastery" as the foundation of a system supporting individual rights.
Early Christian sects such as the Waldensians displayed libertarian attitudes. In 17th-century England, libertarian ideas began to take modern form in the writings of the Levellers and John Locke. In the middle of that century, opponents of royal power began to be called Whigs, or sometimes simply Opposition or Country, as opposed to Court writers.
During the 18th century and Age of Enlightenment, liberal ideas flourished in Europe and North America. Libertarians of various schools were influenced by liberal ideas. For philosopher Roderick T. Long, libertarians "share a common—or at least an overlapping—intellectual ancestry. [Libertarians] [...] claim the seventeenth century English Levellers and the eighteenth century French Encyclopedists among their ideological forebears; and [...] usually share an admiration for Thomas Jefferson and Thomas Paine".

John Locke greatly influenced both libertarianism and the modern world in his writings published before and after the English Revolution of 1688, especially A Letter Concerning Toleration (1667), Two Treatises of Government (1689) and An Essay Concerning Human Understanding (1690). In the text of 1689, he established the basis of liberal political theory, i.e. that people's rights existed before government; that the purpose of government is to protect personal and property rights; that people may dissolve governments that do not do so; and that representative government is the best form to protect rights.
The United States Declaration of Independence was inspired by Locke in its statement: "[T]o secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed. That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it". According to American historian Bernard Bailyn, during and after the American Revolution, "the major themes of eighteenth-century libertarianism were brought to realization" in constitutions, bills of rights, and limits on legislative and executive powers, including limits on starting wars.
According to Murray Rothbard, the libertarian creed emerged from the liberal challenges to an "absolute central State and a king ruling by divine right on top of an older, restrictive web of feudal land monopolies and urban guild controls and restrictions" as well as the mercantilism of a bureaucratic warfaring state allied with privileged merchants. The object of liberals was individual liberty in the economy, in personal freedoms and civil liberty, separation of state and religion and peace as an alternative to imperial aggrandizement. He cites Locke's contemporaries, the Levellers, who held similar views. Also influential were the English Cato's Letters during the early 1700s, reprinted eagerly by American colonists who already were free of European aristocracy and feudal land monopolies.
In January 1776, only two years after coming to America from England, Thomas Paine published his pamphlet Common Sense calling for independence for the colonies. Paine promoted liberal ideas in clear and concise language that allowed the general public to understand the debates among the political elites. Common Sense was immensely popular in disseminating these ideas, selling hundreds of thousands of copies. Paine would later write the Rights of Man and The Age of Reason and participate in the French Revolution. Paine's theory of property showed a "libertarian concern" with the redistribution of resources.
In 1793, William Godwin wrote a libertarian philosophical treatise titled Enquiry Concerning Political Justice and its Influence on Morals and Happiness which criticized ideas of human rights and of society by contract based on vague promises. He took liberalism to its logical anarchic conclusion by rejecting all political institutions, law, government and apparatus of coercion as well as all political protest and insurrection. Instead of institutionalized justice, Godwin proposed that people influence one another to moral goodness through informal reasoned persuasion, including in the associations they joined as this would facilitate happiness.
Libertarian socialism (1857–1980s)
Anarchist communist philosopher Joseph Déjacque was the first person to describe himself as a libertarian in an 1857 letter. Unlike mutualist anarchist philosopher Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, he argued that "it is not the product of his or her labor that the worker has a right to, but to the satisfaction of his or her needs, whatever may be their nature". According to anarchist historian Max Nettlau, the first use of the term libertarian communism was in November 1880, when a French anarchist congress employed it to identify its doctrines more clearly. The French anarchist journalist Sébastien Faure started the weekly paper Le Libertaire (The Libertarian) in 1895.

The revolutionary wave of 1917–1923 saw the active participation of anarchists in Russia and Europe. Russian anarchists participated alongside the Bolsheviks in both the February and October 1917 revolutions. However, Bolsheviks in central Russia quickly began to imprison or drive underground the libertarian anarchists. Many fled to Ukraine, where they fought for the Makhnovshchina in the Russian Civil War against the White movement, monarchists and other opponents of revolution and then against Bolsheviks as part of the Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine led by Nestor Makhno, who established an anarchist society in the region. The victory of the Bolsheviks damaged anarchist movements internationally as workers and activists joined Communist parties. In France and the United States, for example, members of the major syndicalist movements of the CGT and IWW joined the Communist International.
With the rise of fascism in Europe between the 1920s and the 1930s, anarchists began to fight fascists in Italy, in France during the February 1934 riots and in Spain where the CNT (Confederación Nacional del Trabajo) boycott of elections led to a right-wing victory and its later participation in voting in 1936 helped bring the popular front back to power. This led to a ruling class attempted coup and the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939). Gruppo Comunista Anarchico di Firenze held that during the early twentieth century, the terms libertarian communism and anarchist communism became synonymous within the international anarchist movement as a result of the close connection they had in Spain (anarchism in Spain), with libertarian communism becoming the prevalent term.

Libertarian socialism reached its apex of popularity with the Spanish Revolution of 1936, during which libertarian socialists led "the largest and most successful revolution against capitalism to ever take place in any industrial economy". During the revolution, the means of production were brought under workers' control and worker cooperatives formed the basis for the new economy. According to Gaston Leval, the CNT established an agrarian federation in the Levante that encompassed 78% of Spain's most arable land. The regional federation was populated by 1,650,000 people, 40% of whom lived on the region's 900 agrarian collectives, which were self-organised by peasant unions. Although industrial and agricultural production was at its highest in the anarchist-controlled areas of the Spanish Republic, and the anarchist militias displayed the strongest military discipline, liberals and communists alike blamed the "sectarian" libertarian socialists for the defeat of the Republic in the Spanish Civil War. These charges have been disputed by contemporary libertarian socialists, such as Robin Hahnel and Noam Chomsky, who have accused such claims of lacking substantial evidence.
During the autumn of 1931, the "Manifesto of the 30" was published by militants of the anarchist trade union CNT and among those who signed it there was the CNT General Secretary (1922–1923) Joan Peiro, Ángel Pestaña CNT (General Secretary in 1929) and Juan Lopez Sanchez. They were called treintismo and they were calling for libertarian possibilism which advocated achieving libertarian socialist ends with participation inside structures of contemporary parliamentary democracy. In 1932, they established the Syndicalist Party, which participated in the 1936 Spanish general elections and proceeded to be a part of the leftist coalition of parties known as the Popular Front obtaining two congressmen (Pestaña and Benito Pabon). In 1938, Horacio Prieto, general secretary of the CNT, proposed that the Iberian Anarchist Federation transform itself into the Libertarian Socialist Party and that it participate in the national elections.

The Manifesto of Libertarian Communism was written in 1953 by Georges Fontenis for the Federation Communiste Libertaire of France. It is one of the key texts of the anarchist-communist current known as platformism. In 1968, the International of Anarchist Federations was founded during an international anarchist conference in Carrara, Italy to advance libertarian solidarity. It wanted to form "a strong and organized workers movement, agreeing with the libertarian ideas". In the United States, the Libertarian League was founded in New York City in 1954 as a left-libertarian political organization building on the Libertarian Book Club. Members included Sam Dolgoff, Russell Blackwell, Dave Van Ronk, Enrico Arrigoni and Murray Bookchin.
In Australia, the Sydney Push was a predominantly left-wing intellectual subculture in Sydney from the late 1940s to the early 1970s which became associated with the label Sydney libertarianism. Well known associates of the Push include Jim Baker, John Flaus, Harry Hooton, Margaret Fink, Sasha Soldatow, Lex Banning, Eva Cox, Richard Appleton, Paddy McGuinness, David Makinson, Germaine Greer, Clive James, Robert Hughes, Frank Moorhouse and Lillian Roxon. Amongst the key intellectual figures in Push debates were philosophers David J. Ivison, George Molnar, Roelof Smilde, Darcy Waters and Jim Baker, as recorded in Baker's memoir Sydney Libertarians and the Push, published in the libertarian Broadsheet in 1975. An understanding of libertarian values and social theory can be obtained from their publications, a few of which are available online.
In 1969, French platformist anarcho-communist Daniel Guérin published an essay in 1969 called "Libertarian Marxism?" in which he dealt with the debate between Karl Marx and Mikhail Bakunin at the First International. Libertarian Marxist currents often draw from Marx and Engels' later works, specifically the Grundrisse and The Civil War in France.
Libertarianism in the United States (1943–1980s)
H. L. Mencken and Albert Jay Nock were the first prominent figures in the United States to describe themselves as libertarian as synonym for liberal. They believed that Franklin D. Roosevelt had co-opted the word liberal for his New Deal policies which they opposed and used libertarian to signify their allegiance to classical liberalism, individualism and limited government.
According to David Boaz, in 1943 three women "published books that could be said to have given birth to the modern libertarian movement". Isabel Paterson's The God of the Machine, Rose Wilder Lane's The Discovery of Freedom and Ayn Rand's The Fountainhead each promoted individualism and capitalism. None of the three used the term libertarianism to describe their beliefs and Rand specifically rejected the label, criticizing the burgeoning American libertarian movement as the "hippies of the right". Rand accused libertarians of plagiarizing ideas related to her own philosophy of Objectivism and yet viciously attacking other aspects of it.
In 1946, Leonard E. Read founded the Foundation for Economic Education (FEE), an American nonprofit educational organization which promotes the principles of laissez-faire economics, private property and limited government. According to Gary North, the FEE is the "granddaddy of all libertarian organizations".
Karl Hess, a speechwriter for Barry Goldwater and primary author of the Republican Party's 1960 and 1964 platforms, became disillusioned with traditional politics following the 1964 presidential campaign in which Goldwater lost to Lyndon B. Johnson. He and his friend Murray Rothbard, an Austrian School economist, founded the journal Left and Right: A Journal of Libertarian Thought, which was published from 1965 to 1968, with George Resch and Leonard P. Liggio. In 1969, they edited The Libertarian Forum which Hess left in 1971.
The Vietnam War split the uneasy alliance between growing numbers of American libertarians and conservatives who believed in limiting liberty to uphold moral virtues. Libertarians opposed to the war joined the draft resistance and peace movements as well as organizations such as Students for a Democratic Society (SDS). In 1969 and 1970, Hess joined with others, including Murray Rothbard, Robert LeFevre, Dana Rohrabacher, Samuel Edward Konkin III and former SDS leader Carl Oglesby to speak at two conferences which brought together activists from both the New Left and the Old Right in what was emerging as a nascent libertarian movement. Rothbard ultimately broke with the left, allying himself with the burgeoning paleoconservative movement. He criticized the tendency of these libertarians to appeal to "'free spirits,' to people who don't want to push other people around, and who don't want to be pushed around themselves" in contrast to "the bulk of Americans" who "might well be tight-assed conformists, who want to stamp out drugs in their vicinity, kick out people with strange dress habits, etc." Rothbard emphasized that this was relevant as a matter of strategy as the failure to pitch the libertarian message to Middle America might result in the loss of "the tight-assed majority". This left-libertarian tradition has been carried to the present day by Konkin's agorists, contemporary mutualists such as Kevin Carson, Roderick T. Long and others such as Gary Chartier Charles W. Johnson Sheldon Richman, Chris Matthew Sciabarra and Brad Spangler.

In 1971, a small group led by David Nolan formed the Libertarian Party, which has run a presidential candidate every election year since 1972. Other libertarian organizations, such as the Center for Libertarian Studies and the Cato Institute, were also formed in the 1970s. Philosopher John Hospers, a one-time member of Rand's inner circle, proposed a non-initiation of force principle to unite both groups, but this statement later became a required "pledge" for candidates of the Libertarian Party and Hospers became its first presidential candidate in 1972.
Modern libertarianism gained significant recognition in academia with the publication of Harvard University professor Robert Nozick's Anarchy, State, and Utopia in 1974, for which he received a National Book Award in 1975. In response to John Rawls' A Theory of Justice, Nozick's book supported a minimal state (also called a nightwatchman state by Nozick) on the grounds that the ultraminimal state arises without violating individual rights and the transition from an ultraminimal state to a minimal state is morally obligated to occur.
In the early 1970s, Rothbard wrote: "One gratifying aspect of our rise to some prominence is that, for the first time in my memory, we, 'our side,' had captured a crucial word from the enemy. 'Libertarians' had long been simply a polite word for left-wing anarchists, that is for anti-private property anarchists, either of the communist or syndicalist variety. But now we had taken it over". The project of spreading libertarian ideals in the United States has been so successful that some Americans who do not identify as libertarian seem to hold libertarian views. Since the resurgence of neoliberalism in the 1970s, this modern American libertarianism has spread beyond North America via think tanks and political parties.
In a 1975 interview with Reason, California Governor Ronald Reagan appealed to libertarians when he stated to "believe the very heart and soul of conservatism is libertarianism". Libertarian Republican Ron Paul supported Reagan's 1980 presidential campaign, being one of the first elected officials in the nation to support his campaign and actively campaigned for Reagan in 1976 and 1980. However, Paul quickly became disillusioned with the Reagan administration's policies after Reagan's election in 1980 and later recalled being the only Republican to vote against Reagan budget proposals in 1981. In the 1980s, libertarians such as Paul and Rothbard criticized President Reagan, Reaganomics and policies of the Reagan administration for, among other reasons, having turned the United States' big trade deficit into debt and the United States became a debtor nation for the first time since World War I under the Reagan administration. Rothbard argued that the presidency of Reagan has been "a disaster for libertarianism in the United States" and Paul described Reagan himself as "a dramatic failure".
Contemporary libertarianism
Contemporary libertarian socialism

A surge of popular interest in libertarian socialism occurred in Western nations during the 1960s and 1970s. Anarchism was influential in the counterculture of the 1960s and anarchists actively participated in the protests of 1968 which included students and workers' revolts. In 1968, the International of Anarchist Federations was founded in Carrara, Italy during an international anarchist conference held there in 1968 by the three existing European federations of France, the Italian and the Iberian Anarchist Federation as well as the Bulgarian Anarchist Federation in French exile.
Around the turn of the 21st century, libertarian socialism grew in popularity and influence as part of the anti-war, anti-capitalist and anti-globalisation movements. Anarchists became known for their involvement in protests against the meetings of the World Trade Organization (WTO), Group of Eight and the World Economic Forum. Some anarchist factions at these protests engaged in rioting, property destruction and violent confrontations with police. These actions were precipitated by ad hoc, leaderless, anonymous cadres known as black blocs and other organizational tactics pioneered in this time include security culture, affinity groups and the use of decentralized technologies such as the Internet. A significant event of this period was the confrontations at WTO conference in Seattle in 1999. For English anarchist scholar Simon Critchley, "contemporary anarchism can be seen as a powerful critique of the pseudo-libertarianism of contemporary neo-liberalism. One might say that contemporary anarchism is about responsibility, whether sexual, ecological or socio-economic; it flows from an experience of conscience about the manifold ways in which the West ravages the rest; it is an ethical outrage at the yawning inequality, impoverishment and disenfranchisment that is so palpable locally and globally". This might also have been motivated by "the collapse of 'really existing socialism' and the capitulation to neo-liberalism of Western social democracy".
Since the end of the Cold War, there have been at least two major experiments in libertarian socialism: the Zapatista uprising in Mexico, during which the Zapatista Army of National Liberation (EZLN) enabled the formation of a self-governing autonomous territory in the Mexican state of Chiapas; and the Rojava Revolution in Syria, which established the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES) as a "libertarian socialist alternative to the colonially established state boundaries in the Middle East."
In 2022, student activist and self-described libertarian socialist Gabriel Boric became head of state of Chile after winning the 2021 Chilean presidential election with the Apruebo Dignidad coalition.
Contemporary libertarianism in the United States
In the United States, polls (circa 2006) found that the views and voting habits of between 10% and 20%, or more, of voting age Americans might be classified as "fiscally conservative and socially liberal, or libertarian". This was based on pollsters' and researchers' defining libertarian views as fiscally conservative and socially liberal (based on the common United States meanings of the terms) and against government intervention in economic affairs and for expansion of personal freedoms. In a 2015 Gallup poll, this figure had risen to 27%. A 2015 Reuters poll found that 23% of American voters self-identified as libertarians, including 32% in the 18–29 age group. Through twenty polls on this topic spanning thirteen years, Gallup found that voters who are libertarian on the political spectrum ranged from 17–23% of the United States electorate. However, a 2014 Pew Poll found that 23% of Americans who identify as libertarians have no idea what the word means. In this poll, 11% of respondents both identified as libertarians and understand what the term meant.
In 2001, an American political migration movement, called the Free State Project, was founded to recruit at least 20,000 libertarians to move to a single low-population state (New Hampshire, was selected in 2003) in order to make the state a stronghold for libertarian ideas. As of May 2022, approximately 6,232 participants have moved to New Hampshire for the Free State Project.

2009 saw the rise of the Tea Party movement, an American political movement known for advocating a reduction in the United States national debt and federal budget deficit by reducing government spending and taxes, which had a significant libertarian component despite having contrasts with libertarian values and views in some areas such as free trade, immigration, nationalism and social issues. A 2011 Reason-Rupe poll found that among those who self-identified as Tea Party supporters, 41 percent leaned libertarian and 59 percent socially conservative. Named after the Boston Tea Party, it also contained populist elements. By 2016, Politico noted that the Tea Party movement was essentially completely dead; however, the article noted that the movement seemed to die in part because some of its ideas had been absorbed by the mainstream Republican Party.
In 2012, anti-war and pro-drug liberalization presidential candidates such as Libertarian Republican Ron Paul and Libertarian Party candidate Gary Johnson raised millions of dollars and garnered millions of votes despite opposition to their obtaining ballot access by both Democrats and Republicans. The 2012 Libertarian National Convention saw Johnson and Jim Gray being nominated as the 2012 presidential ticket for the Libertarian Party, resulting in the most successful result for a third-party presidential candidacy since 2000 and the best in the Libertarian Party's history by vote number. Johnson received 1% of the popular vote, amounting to more than 1.2 million votes. Johnson has expressed a desire to win at least 5 percent of the vote so that the Libertarian Party candidates could get equal ballot access and federal funding, thus subsequently ending the two-party system. The 2016 Libertarian National Convention saw Johnson and Bill Weld nominated as the 2016 presidential ticket and resulted in the most successful result for a third-party presidential candidacy since 1996 and the best in the Libertarian Party's history by vote number. Johnson received 3% of the popular vote, amounting to more than 4.3 million votes. Following the 2022 Libertarian National Convention, the Mises Caucus, a paleolibertarian faction, became the dominant faction on the Libertarian National Committee.
Chicago school of economics economist Milton Friedman made the distinction between being part of the American Libertarian Party and "a libertarian with a small 'l'," where he held libertarian values but belonged to the American Republican Party.
Contemporary libertarianism in Argentina
In 2023, Argentine economist Javier Milei became the first open libertarian head of state, after winning that year's general election with the La Libertad Avanza coalition.
Contemporary libertarian organizations
Current international anarchist federations which identify themselves as libertarian include the International of Anarchist Federations, the International Workers' Association and International Libertarian Solidarity. The largest organized anarchist movement today is in Spain, in the form of the Confederación General del Trabajo (CGT) and the Confederación Nacional del Trabajo (CNT). CGT membership was estimated to be around 100,000 for 2003. Other active syndicalist movements include the Central Organisation of the Workers of Sweden and the Swedish Anarcho-syndicalist Youth Federation in Sweden, the Unione Sindacale Italiana in Italy, Workers Solidarity Alliance in the United States, and Solidarity Federation in the United Kingdom. The revolutionary industrial unionist Industrial Workers of the World claiming 2,000 paying members as well as the International Workers' Association, remain active. In the United States, there exists the Common Struggle – Libertarian Communist Federation.
Since the 1950s, many American libertarian organizations have adopted a free-market stance as well as supporting civil liberties and non-interventionist foreign policies. These include the Ludwig von Mises Institute, Francisco Marroquín University, the Foundation for Economic Education, Center for Libertarian Studies, the Cato Institute and Liberty International. The activist Free State Project, formed in 2001, works to bring 20,000 libertarians to New Hampshire to influence state policy. Active student organizations include Students for Liberty and Young Americans for Liberty. A number of countries have libertarian parties that run candidates for political office. In the United States, the Libertarian Party was formed in 1972 and is the third largest American political party, with 511,277 voters (0.46% of total electorate) registered as Libertarian in the 31 states that report Libertarian registration statistics and Washington, D.C.
Criticism
Criticism of libertarianism includes ethical, economic, environmental, pragmatic and philosophical concerns, especially in relation to right-libertarianism, including the view that it has no explicit theory of liberty. It has been argued that laissez-faire capitalism does not necessarily produce the best or most efficient outcome, nor does its philosophy of individualism and policies of deregulation prevent the abuse of natural resources.
Critics have accused libertarianism of promoting "atomistic" individualism that ignores the role of groups and communities in shaping an individual's identity. Libertarians have responded by denying that they promote this form of individualism, arguing that recognition and protection of individualism does not mean the rejection of community living. Libertarians also argue that they are simply against individuals' being forced to have ties with communities and that individuals should be allowed to sever ties with communities they dislike and form new communities instead.
Critics such as Corey Robin describe this type of libertarianism as fundamentally a reactionary conservative ideology united with more traditionalist conservative thought and goals by a desire to enforce hierarchical power and social relations. Similarly, Nancy MacLean has argued that libertarianism is a radical right ideology that has stood against democracy. According to MacLean, libertarian-leaning Charles and David Koch have used anonymous, dark money campaign contributions, a network of libertarian institutes and lobbying for the appointment of libertarian, pro-business judges to United States federal and state courts to oppose taxes, public education, employee protection laws, environmental protection laws and the New Deal Social Security program.
Conservative philosopher Russell Kirk argued that libertarians "bear no authority, temporal or spiritual" and do not "venerate ancient beliefs and customs, or the natural world, or [their] country, or the immortal spark in [their] fellow men." Libertarians have responded by saying that they do venerate these ancient traditions, but are against the law's being used to force individuals to follow them.
See also
- Classical liberalism
- Christian libertarianism
- Fusionism
- Green libertarianism
- Libertarian feminism
- List of libertarian political ideologies
- Neoclassical liberalism
- Non-aggression principle
- Objectivism
- Outline of libertarianism
- Paleolibertarianism
- "Property is theft!"
- Refusal of work
- "Taxation is theft!"
- Technolibertarianism