GABA reuptake inhibitor
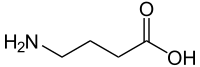
A GABA reuptake inhibitor (GRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) by blocking the action of the gamma-Aminobutyric acid transporters (GATs). This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of GABA and therefore an increase in GABAergic neurotransmission.
Indications
GRIs may be used in the clinical treatment of seizures, convulsions, or epilepsy as anticonvulsants/antiepileptics, anxiety disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social phobia (SP) also known as social anxiety disorder (SAD), and panic disorder (PD) as anxiolytics, insomnia as hypnotics, muscle tremors or spasms as muscle relaxants, and chronic pain as analgesics. They may also potentially be used as anesthetics in surgery.
Effects
GRIs can induce a wide range of psychological and physiological effects, including:
- general and subjective alteration in consciousness
- dizziness
- blurry vision
- diplopia or double vision
- nystagmus or involuntary eye movements
- amblyopia or "lazy eye"
- tinnitus or "ear ringing"
- sedation
- drowsiness or somnolence
- narcolepsy
- tiredness or weakness
- fatigue or lethargy
- aches and pains
- headache
- nausea and vomiting
- gastrointestinal disturbances
- shakiness
- disorientation
- diminished awareness
- impaired attention
- focus and concentration
- decreased drive and motivation
- stuttering and slurring of speech
- confusion
- cognitive and memory impairment
- mood lift or drop
- depression
- anxiolysis
- disinhibition
- stress reduction
- euphoria or dysphoria
- irritability
- aggression
- anger or rage
- increased appetite and subsequent weight gain
- ataxia or impaired coordination and balance
- muscle relaxation
- trembling or muscle tremors and spasms
- paresthesia or "pins and needles"
- analgesia
- respiratory depression
- dyspnea or shortness of breath
Many of these properties are dependent on whether the GRI in question is capable of crossing the blood-brain-barrier (BBB). Those that do not will only produce peripheral effects.
GRIs such as CI-966 have been characterized as hallucinogens with effects analogous to those of the GABAA receptor agonist muscimol (a constituent of Amanita muscaria (fly agaric) mushrooms) when administered at sufficient doses.
Overdose
At very high doses characterized by overdose, a number of symptoms may come to prominence, including:
- severe cognitive deficit to the point of acute retardation
- anterograde or retrograde amnesia
- drooling
- piloerection or "goose bumps"
- agitation or restlessness
- flailing
- thrashing and screaming
- unintentional or accidental injury
- delirium
- hallucinations
- myoclonus
- dystonia
- paralysis
- stupor
- faintness or loss of consciousness
- seizures or convulsions
- status epilepticus
- coma and respiratory arrest or cessation of breathing
- brain damage
- death
List of GRIs
- CI-966
- Deramciclane (EGIS-3886)
- Gabaculine
- Guvacine (C10149)
- Nipecotic acid
- NNC 05-2090
- NNC-711
- SKF-89976A
- SNAP-5114
- Tiagabine (Gabitril)
- Hyperforin